

You don’t use ln terms because the temperature is constant. Here the entropy of the lake uses a different tactic. Now what happens to the entropy of the lake? The lake has constant temperature of 288K. Then the final section is where the temperature goes from 0 to 10 C. There is the part where the temperature goes from -10 to 0 C, then there is the heat of fusion of the water section. Notice there are three parts to the above problem. If you notice, we don't have an expression for the way entropy changes due to. For freezing we calculate entropy change. Troutons rule estimates that it is 83-93 J mol-1K-1. When we hold temperature constant (an isothermal process), and change one of the other parameters: (1) S P 2 P 1 ( S P)T dP. Most liquids have nearly the same molar entropy of vaporization. Then we use the method of cutting into pieces we talked about earlier. Entropy is typically considered a function of temperature and either volume or pressure. We first assume the final temperature remains constant at 15 C. Using this as a reference point, the entropy of a substance can be obtained by measuring the heat required to raise the temperature a given amount, using a. This is a problem out of the Serway Physics book problems section. Calculate the change in entropy of the cube-lake system as the ice cube comes to thermal equilibrium with the lake. Trying to add steps, like taking the temperature difference of an entire process of several steps and dividing the average heat value of the whole process by this temperature change won’t accomplish anything.įor our first example we have a 10 g ice cube at -10 C that is put into a lake whose temperature is 15 C. This cut and paste method is the only way to get the correct answer. Basically you cut up each part of a phase diagram into a certain section and solve for the entropy of each of the sections by themselves and then add them together at the end. Generally you use the ln formula when the temperature changes and you use mL for fusion changes. According to the formula, S k ln W where k, the. If the temperature doesn’t change you make T constant, but the heat could change under certain circumstances like described earlier. Using statistical mechanics of the gas phase, entropy can be estimated by using Boltzmanns formula.
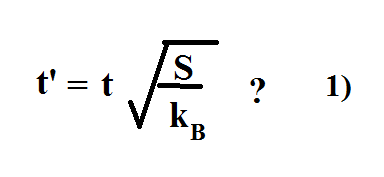
When do you use mCvln(Tf-Ti) to find the heat? You use this if the temperature changes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
